You are in the right place if you’re looking for a comprehensive guide to Google Ads language targeting.
As an experienced digital marketer, I understand the struggle of trying to reach a global audience without overriding your budget.
With this guide, you will be able to optimize your campaigns for better results by using the unique language Targeting feature on Google Ads.
With my assistance, you will learn how to narrow down your target audience and utilize keywords that suit their language preferences best.
You can bring more customers in and leave behind unsuccessful campaigns! Let’s take your business from good to great with this primer on Google Ads language targeting today.
What is Language Targeting?
Google Ads Language Targeting is a great way to reach the desired demographic for your business.
It allows you to target ads that are tailored for specific languages, which helps narrow down the audience that sees your ads.
There are many benefits to language targeting, including the following:
- Maximizing the reach of your ads: With language targeting, you can reach more people who are likely to be interested in your product or service.
- Cost savings: Because you only pay for the clicks from those who speak your targeted language, you save money on advertising costs.
- Better conversion rates: Ads that use a person’s native language are more likely to be successful and result in more conversions.
- Improving click-through rates: Ads in the right language will have a higher click-through rate and help you get more out of your ad spend.
- Enhancing customer segmentation: Language targeting helps you segment your customers based on their language preferences, allowing you to tailor ads to different groups.
By using Google Ads language targeting, you can ensure that your ads reach the right audience.
Using this tool allows you to aim at users who speak different languages to help drive targeted traffic to your website.
Whether it’s Spanish, Chinese, French, or any other language, you can make sure that viewers of your ads understand them regardless of the language they speak.
Additionally, with more advanced settings available, you can be sure that the right person sees the right message.
This way, you don’t end up wasting money paying for ads that won’t be seen or understood by anyone who isn’t within the target audience.
For example:
You could target Spanish-speaking people with a Spanish version of your ad and English-speaking people with an English version.
This ensures that you can reach the right people in their native language, which can help increase conversion rates and save you money on advertising costs.
What are Multilingual Google Ads?
Multilingual Google Ads is a digital marketing strategy that uses language targeting to help you reach people who speak different languages.
You can create multiple versions of an ad that are tailored for specific audiences and target them with the same message but in their native language.
Multilingual Google Ads is a great tool for businesses who want to reach foreign audiences with their content.
- Google Ads Language Targeting helps you reach a global audience without exceeding your budget.
- With language targeting, you can target ads that are tailored for specific languages to narrow down the audience.
- The benefits of language targeting include maximizing the reach of your ads, cost savings, better conversion rates and click-through rates, as well as enhanced customer segmentation.
- Multilingual Google Ads help you create multiple versions of an ad tailored to specific audiences and target them with the same message but in their native language.
- Using multilingual ads is a great way to reach foreign audiences with your content.
These ads allow advertisers to specify which language or group of languages that their ads should be served to – over 50 different languages!
By leveraging the power of Google’s own language targeting technology, businesses can ensure their advertisements appear in search results for users looking for them in their native tongue.
This adds convenience and relevance, leading to higher chances of successful conversions. Using multilingual Google Ads is a smart way for companies with cross-border aspirations to better take advantage of the internet’s global reach.
By targeting different language speakers, you can ensure your message reaches people in their native language, which increases the likelihood of them engaging with your ad and encourages them to move further through the sales funnel.
How Does Google Detect a User’s Language?
Google has developed a sophisticated method for targeting its ads by language.
Through a combination of machine learning algorithms and data signals, Google can detect which language(s) a user speaks, allowing it to serve up appropriate Search Network ads on the search engine results page as well as Display Network ads on websites.
As part of its language detection process, Google considers clues such as:
- Browsing history: Do you visit websites about certain languages, countries, or cultures?
- Device settings: Is your device set to display in a different language than your location?
- Location: Are you physically located in a country where another language is spoken?
- Search query: Do you search words in a particular language? Do you search for content relevant to a particular region or culture?
- IP address: Your IP address can give clues to your location.
- Previous interactions with Google Ads: Have you interacted with a certain ad or ads in certain languages in the past?
- System time zone settings: Do you have your system time set to a country or region where another language is spoken?
Google considers all of these signals together and uses them to accurately determine a user’s likely language preference.
For Search Network ads, google analyzes signals such as language detection settings from the browser and search query keywords.
So if a user conducts an international search in French, but their web settings display English, they may see ads in either language.
Google also uses page viewing history on the Display Network to determine which languages to show ads in.
If a user’s recent website visits have continually been in French, for example, then there is a strong indication that display ads should be targeted toward those pages with the same production language.
Overall, Google’s data-driven approach allows for a tailored ad experience while respecting each user’s preferred language.
Language Targeting Vs. Location Targeting
Language targeting and location targeting are crucial elements of digital marketing.
While both are important, they have different goals and should be used in combination to maximize your results.
Language Targeting:
- Allows users to target ads based on the preferred language of a user or customer.
- This allows you to tailor your ad message specifically for the audience you are trying to reach.
- Enables you to save money on advertising costs by targeting a more specific audience.
Language targeting allows you to clearly communicate with customers who may be completely unaware of your products or services and could potentially increase your customer base significantly.
Location Targeting:
- Allows users to target ads with geographical locations in mind.
- This can help you reach people in certain areas that may be interested in your products or services.
- Enables you to tailor ads for regional preferences and local trends.
Location targeting is great if you want to focus on people who live in a certain country, state, or city, as it ensures that only people within those areas will see your ads.
Using a combination of language targeting and location targeting in targeted ad campaigns can be incredibly effective.
Google Ads provides an intuitive tool that allows you to personalize your ads so that they are tailored to their intended audience by region, language, or data about user behavior.
For instance, if you want to market your product to individuals who speak Spanish and live in Mexico, leveraging language and location targeting in Google Ads is key.
This allows you to deliver personalized experiences that appeal more effectively to customers, resulting in a higher return on invested funds and a greater impact on sales numbers.
Ultimately, this type of targeted ad campaign can have a hugely positive effect on the success of any business venture.
How Does Language Targeting Work?
Google Ads’ language targeting allows companies to display their ads in multiple languages and target different countries, regions, and localities where certain languages are spoken.
This enables companies to expand their reach beyond users who have limited English literacy or simply prefer interacting in their preferred language, ensuring that campaigns speak more closely to local cultural contexts.
When crafting your Google ad on either the Search Network or Display Network, remember to consider the target language of your ad.
Unless specifically targeted, Google defaults to “All languages” for viewing the ad.
Google provides an extensive list of languages available for targeting, with over 50 optionsspanning across diverse cultures, such as:
- Spanish
- French
- German
- Korean
- and Vietnamese
Additionally, this same set of languages supported by language targeting is also applicable to creating your actual advertisement copy.
This means that if you write content in an unsupported language like Icelandic or Bengali, then unfortunately, it will not be approved by Google for display users.
Once you have selected the language you want to target, you can also refine your search by location.
This helps you identify the right customer base in order to make sure the intended audience sees your ads.
Should You Translate Your Google Ads?
The translation is an essential step when it comes to ensuring the success of your Google Ads.
If you’re running a Google Ad, language targeting should be at the top of your list.
Doing so can make a huge difference in how effective your ads will be.
Having ads that are written in the native language of your target demographic is essential in order to fully understand the message that you want to convey.
Translating the content of your ads and including multiple languages can help ensure it reaches the right audience and resonates with them.
Knowing the local language and being able to translate your Google Ads properly can be huge differentiators from competitors that will result in stronger ROI for your campaigns.
Google Ads language targeting takes more than running your copy through google translate.
There are a few more steps to running a successful multilingual campaign:
- Localize your keywords: Make sure you’re using words that are relevant to the language and culture of your target audience. Literal translations often sound awkward to native speakers and can lead to embarrassing translation mistakes that will haunt you for years.
- Design for each culture: Customize elements such as color schemes, images, and graphics to appeal to a particular cultural group. This will help create an ad that resonates with the customer and encourages them to click.
- Test your ad with native speakers: Have a native speaker review and test your ad to make sure it conveys the right message. This will help you avoid any misunderstandings that could arise due to a literal translation of your ad copy.
- Optimize your landing pages: Ensure that they are translated into the same language as your ads so that customers have a seamless experience. This will also help you maximize your conversion rates.
- Make sure your copy fits Google’s character limits: Google Ads has specific character limits for ads which may be different depending on the language you’re targeting. Be sure to double check that your ad copy fits within these limits before submitting it for review.
- Test, test, test: Test different versions of your ads to see which ones perform the best in each language group.
Google Ads language targeting is an effective way to reach new markets, but it’s important to understand the nuances of each language you’re targeting before launching a campaign.
To ensure your ads get the most traction, take into account language specifics and cultural understanding.
Be sure to do proper keyword research and use accurate translation sources. Keyword research is extremely useful for general SEO, so there’s no harm in extending your research to other languages.
To save time and money during the process, you can utilize a free translation tool online to create a rough draft of your ad campaign or check how certain phrases and words may look when published.
How Do You Change the Language Targeting In Google Ads?
Now that you know the basics of Google Ads language targeting, let’s take a look at how to actually change the language and location settings in your campaigns.
The process is fairly simple and should only take a few minutes.
Select Languages Your Customers Speak
When it comes to Google Ads, language targeting allows you to pick the languages that best fit your customers.
Whether you’re creating a new Search Network or Display Network ad, setting up your language targeting is easy – simply fill out the area where it asks what languages your audience speaks.
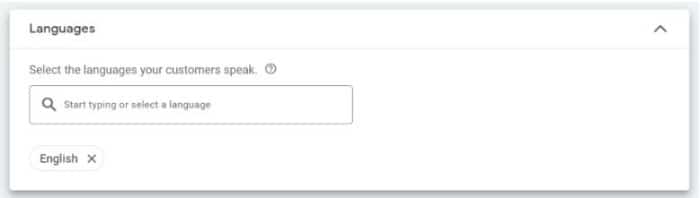
For more precise targeting, especially for search ads, you can set up negative keywords to limit which search engine results from pages or display network websites your ad appears on.
For example:
Let’s say you’re targeting Spanish-speaking customers. You can exclude any results that are in English, even if they contain some of the same keywords as your ad.
By taking a few extra moments to change the language targeting in Google Ads, you can ensure that your ads are seen only by those who speak the corresponding language – increasing customer engagement and improving customer satisfaction and conversions.
Edit Your Campaign Settings to Include Other Locations
With the help of location targeting options, you can choose different geographical locations where you want potential customers to see your Google Ads.
This will enable you to reach out to more potential customers and increase your ad’s visibility.
Changing the location targeting for your Google ad is fairly simple.
Through campaign settings, you can customize the geographical locations in which you want to display your ad.
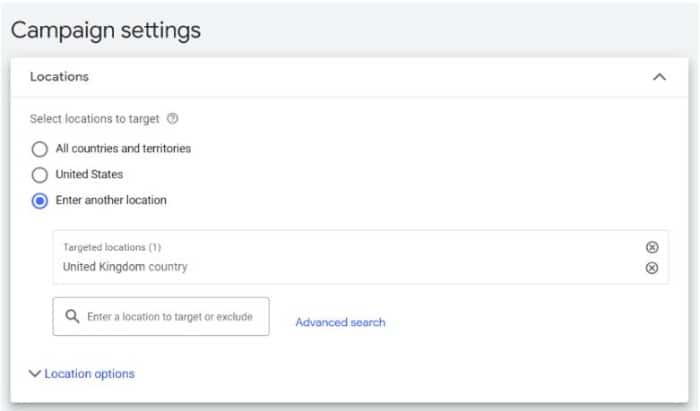
For example, if you want to reach a worldwide audience or only people from specific countries and regions, you can use the location targeting options to select the appropriate areas.
If you need to update the language targeting after creating your ad, you can accomplish this through easy-to-use campaign settings that allow for quick changes.
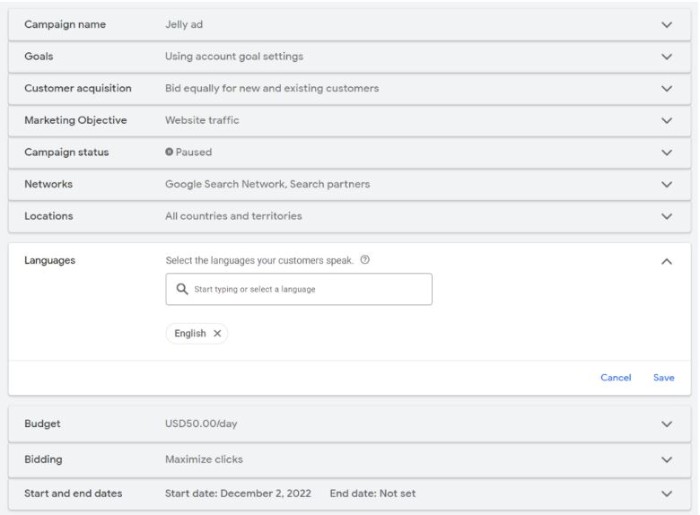
With just a few clicks and some adjustments in specific locations and languages, you can effectively modify the language targeting of your Google advertisement.
Conclusion
Language targeting plays an important part in any successful Google Ads campaign.
With language targeting, you can ensure that your ads are only seen and heard by people who understand the kind of messaging you’re looking to convey.
By pinpointing specific language audiences, you can also save yourself money since you won’t be targeting ads to those who don’t need them.
To conclude, Google ads language targeting is a useful tool that can help to reach global audiences, regardless of what language they speak.
Through careful strategizing and selection of language categories, businesses can effectively market their products and services throughout the world in a variety of languages without having to worry about the expensive costs and manpower associated with manual translation processes.
By taking advantage of this service and marketing across multiple languages, businesses can maximize their potential customer base while keeping their costs reasonable.
With the right implementation strategy in place, Google ads language targeting can be an extremely beneficial tool for international companies who want to engage audience members on an international level.
As you plan out your next steps, one question remains: does language targeting fit into your overall marketing strategy?
Leave your thoughts about language targeting in the comments below and share any questions or insights you may have.
The post originally appeared on following source : Source link

